Upsc DIAGRAMS ( Champions camp)
Join us
Fetch extra marks in each paper of mains
Diagrams flowchart - prepared by candidates selected and interview appeared
For paid promotion contact @msharma99
Join our Sociology channel
@socio300plus
https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VahajMPKbYMLUq Связанные каналы | Похожие каналы
88 979
obunachilar
Kanalda mashhur
MPPSC Pre 2025 Exam Paper Exam Date - 16 February 2025
“The last date for submission for CS(P)-2025 & IFoS(P)-2025 has been extended till 18.02.2025 (...
UKPSC 2024 Mains Hindi Paper.
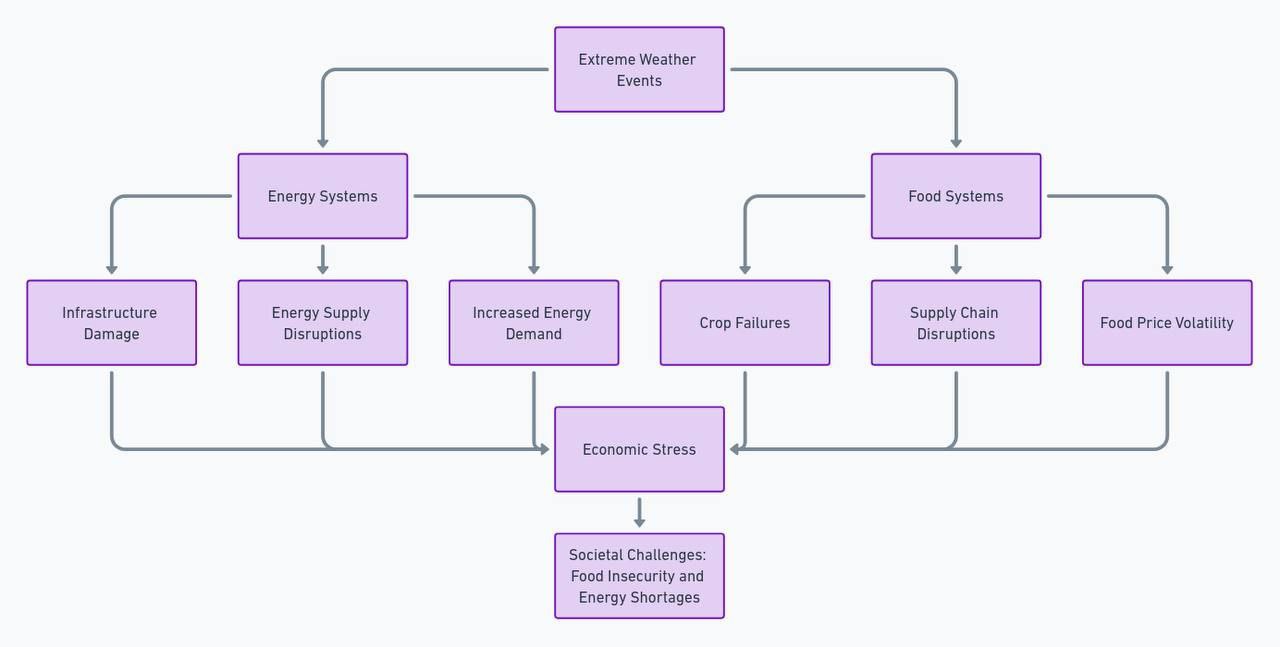
Impact of Extreme weather Events on energy and Food Security Current affairs diagrams
Cgpsc prelims today paper 9 feb 2025




